In the world of the green building certification systems, WELL Building Standard is the most recent rating scheme for sustainable and healthy buildings. The uptake of the WELL is increasing rapidly, especially since 2019.
In recent years, building industry has perceived sustainability in building as meaning of energy efficiency and environmental performance. Most recently, the industry focus has shifted towards a more holistic interpretation of sustainability. Emphasis on the way healthy and liveability indoor spaces support people’s wellbeing and their quality of life is at the top of the agenda.
Then, the pandemic crisis has boost even further people’s awareness on healthy building. The impact the buildings may have on people’s health and wellbeing has never being more evident and important.
But how do we actually measured wellbeing in buildings?
The Well Building Standard is the world’s first evidence-based system designed for measuring, certifying and monitoring building features that impact on health and wellbeing.
Unlike other green building certification schemes, such as LEED, BREEAM, ESTIDAMA, HK BEAM etc., the WELL Building Standard puts health and wellbeing at the centre of design and construction decisions. A great emphasis is given on strategies aimed at enhancing people’s health and wellbeing in building without neglecting the building sustainability performance and the impact on the environment.
Best practices in design and construction are coupled with robust evidence-based medical and scientific research – harnessing the built environment as a vehicle to support human health and wellbeing.
The WELL Building Standard (WELL) is a performance-based system designed for measuring, certifying, and monitoring features of the built environment that impact human health and wellbeing, through air, water, nourishment, light, fitness, comfort and mind.
The WELL Building Standard was founded and developed by Delos Living LLC in 2014.
The WELL is a third-party building certification scheme managed and administered by the International WELL Building Institute (IWBI), in close collaboration with Green Building Certification Institute (GBCI). The GBCI is the party that also administers other leading rating systems such as LEED, SITES, TRUE, etc.
The first version of the pioneering rating system, WELL Building Standard version 1 (WELL v1) , was launched to public in late 2014, as a result of a two-year pilot program and a formal Peer Review process.
The WELL Building Standard v1 is optimised for commercial and institutional offices, and can be applied to 3 type of developments:
- New and Existing Buildings
- New and Existing Interiors
- and Core and Shell Compliance.
WELL v1 also includes a set of pilot standards which are applicable to other building types:
- Retail
- Multifamily Residential
- Education
- Restaurant
- Commercial Kitchen
More recently, a new version of the WELL Building Standard (WELL v2) was released aimed at delivering more thoughtful and intentional spaces that enhance human health and well-being.
WELL v2 draws expertise and experience from a global community of WELL users, practitioners, public health professionals and building scientists.
WELL Building Standard v2 consolidates previous version and pilots schemes into a single rating system, which is designed to accommodate all project types and sectors.
WELL v2 projects fall into two main groups, determined primarily by ownership type:
- Owner-occupied: this is a building mainly occupied by the project owner (which may be different than the building owner).
- WELL Core: the project owner occupies a small portion of the project area and rents/leases most of the space to one or more tenants.
Following the Pandemic crisis, the International WELL Building Institute has introduced the WELL Health-Safety Rating.
The new WELL Health-Safety Rating is a an evidence-based, third-party verified rating system that assists building owners, facility managers and operators in the implementation of best practices for mitigating the spread of COVID-19 and for navigating this crisis and beyond.
The WELL Health-Safety Rating provides building operation and management teams across the industry with an effective tool to take all the necessary steps in order to prioritize the health and safety of their staff, visitors and other stakeholders, while helping guide users in preparing their spaces for re-entry in a post-COVID-19 environment, instilling confidence in occupants and the broader community.
How the WELL Building Standard works
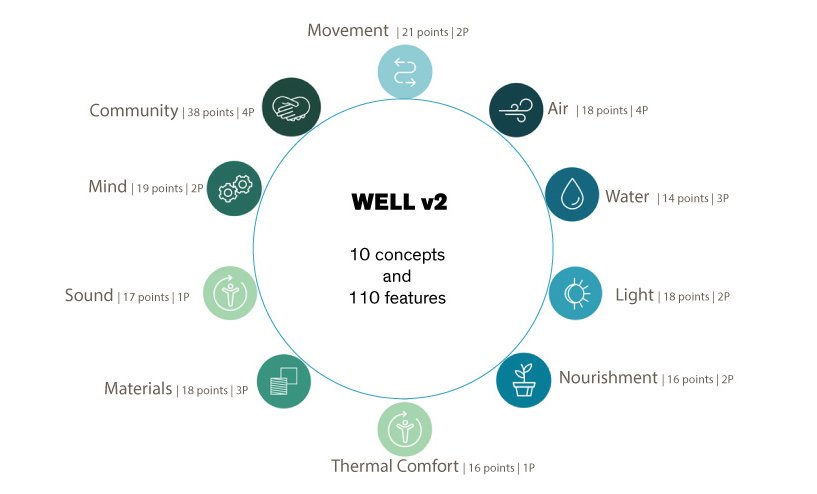
The WELL Building Standard v2 is made-up of 110 features (performance metrics, design strategies, and policies) which are grouped within 10 concepts: Air, Water, Nourishment, Light, Movement, Thermal Comfort, Sound, Materials, Mind and Community.
Preconditions
Preconditions (like LEED prerequisites) represents the core features of the WELL Building Standard. In order to be awarded WELL certification, all applicable Preconditions must be met by the proposed building.
Optimizations
Optimizations provides project teams with optional pathways to meet WELL certification requirements. These optimisation features (like LEED credits) include possible technologies, design strategies, protocols and policies that can be implemented by the owners, designers, engineers, contractors, users and operators. Project teams may identify which optimizations to target and which parts to focus on within each optimization. Each feature is divided into parts, which are tailored to a specific building type.
Each WELL feature (optimization) is assigned a number of points according to its potential impact in addressing a specific health and wellness concern or opportunity for health promotion, and the potential impact of the intervention.
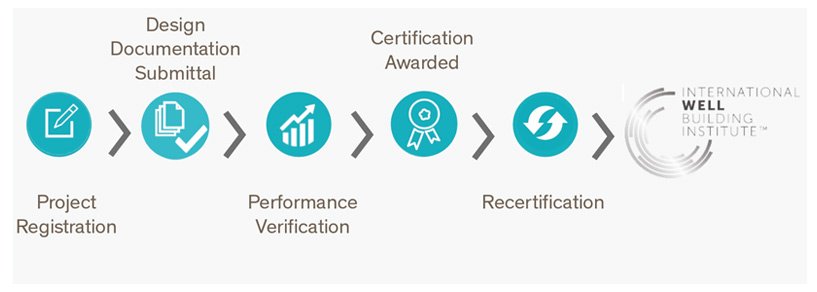
The WELL certification process
Buildings can be awarded WELL certification with Silver, Gold or Platinum rating (with Platinum being the highest achievement). WELL certified buildings require recertification every 3 years.
Similarly to other green building rating systems, also WELL Building Standard v2 is a voluntary certification scheme that operates on a points-based system.
Project teams can pursue no more than 12 points per concept and no more than 100 points total across the ten concepts. 10 additional points are available in the Innovation concept (innovative credits).
Projects must earn a minimum of two points per concept (or at least four points combined in the case of the Air and Thermal Comfort concepts).
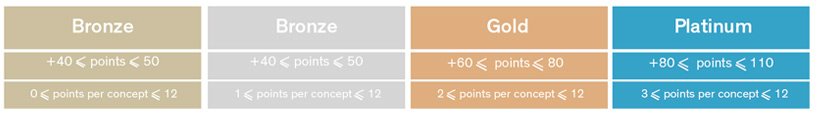
Projects must achieve all preconditions as well as a certain number of points to earn different levels of certification:
- WELL Silver Certification: 50 points.
- WELL Gold Certification: 60 points.
- WELL Platinum Certification: 80 points.
However, for projects pursuing WELL Core Certification pathway (core and shell buildings), a minimum of one point per concept must be earned, and all preconditions must be achieved.
WELL Core certification levels are as follows:
- WELL Core Bronze Certification: 40 points.
- WELL Core Silver Certification: 50 points.
- WELL Core Gold Certification: 60 points.
- WELL Core Platinum Certification: 80 points.
To demonstrate compliance with the pursued WELL feature requirements, project teams need to provide evidence and documentation (i.e. construction documents, product VOC emission testing and certifications).
In order to be granted certification, the building has to be assessed in operation and must successfully pass third-party performance verification testing. This is to ensure and confirm adherence to WELL requirements.
On-site performance verification may include tests to measure air and water quality, as well as sound and light levels.
WELL Accredited Professional (WELL AP)
WELL Accredited Professionals (WELL AP) are building industry professionals who have strong expertise and experience of the WELL frameworks and its application. WELL AP can strategically guide the project team to successful achieve the WELL certification.
However, project teams are not required to include a WELL AP but having a WELL AP as part of a project team will help to address all necessary aspects of WELL and qualifies projects for achievement of a pre-approved innovation feature in WELL.
WELL and healthy building materials
Implementing WELL Building Standard requires project teams to carefully select healthy building materials and products (i.e. indoor finishes, furniture, ventilation systems).
The WELL Materials concept is one of the core pillars of the WELL certification system. Project teams and specifiers are asked to identify building material that minimise human exposure to hazardous chemical ingredients or eliminate toxic compound in indoor spaces. Great emphasis is placed on product data transparency as well as material ingredients that can impact human health and wellbeing.
Building product manufacturers are key to making it easier for designers, architects and specifiers to implement WELL features.
Some forward-thinking manufacturers are already deep-diving into WELL requirements on related products, investing in research and modifying their products in order to offer healthy building solutions to specifiers.
Over the last few months many manufacturers have used Ongreening’s innovative product mapping tool, ProductMAP, to automatically assess their product eligibility and contribution to WELL Building Standard. The mapping process unveils the whole value of the building materials in the context of the WELL certification.
Ongreening’s ProductMAP received the officially endorsement from the International WELL Building Institute as a powerful tool for manufacturers and a unique material databases to help project teams and specifiers in the selection of healthy building materials eligible for their WELL scheme.

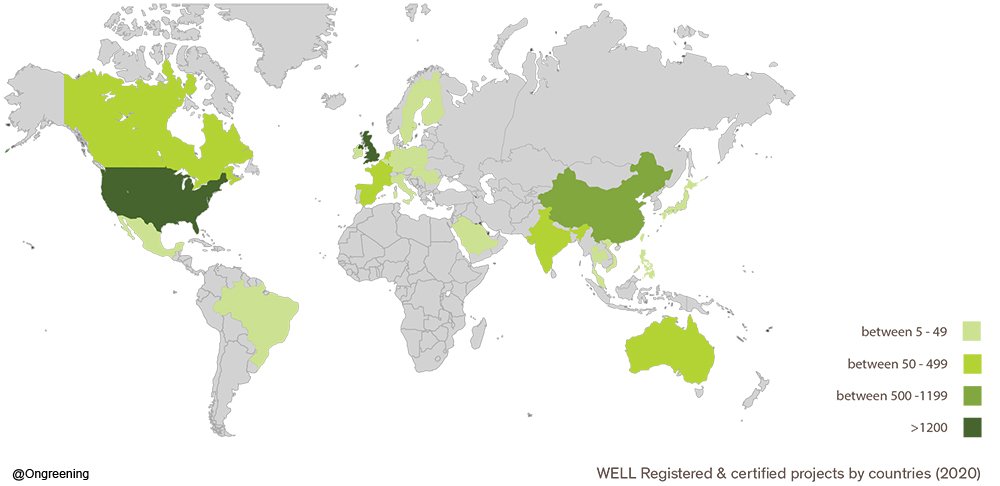
Market Penetration
Since its launch in 2014, the WELL Building Standard has gained a strong market recognition worldwide as an industry-recognised mark of excellence for healthy buildings.
According to IWBI, the WELL Building Standard is currently used in more than 67 countries with more than 400 WELL certified projects worldwide and 5,507 further building currently pursuing WELL certification, for a total of 818 million sqft* (approx. 76 million of square meters).




